

Blog:
Routing Protocol voting


The Routing Protocol is a mechanism to gradually decentralize the network. There are two principal kinds of decentralization the Routing Protocol enables. There is the decentralization of operation, which you can read about in our blog post on staking. And there is the decentralization of decision making, which we will cover in this article.
First of all, a recap of the basics: holders of HMT will be able to lock their HMT in a voting smart contract to receive vHMT, which represents voting power within the network. This is a way to foster community contribution to the network.
Voting power will be related to reputation and stake. Importantly, stake cannot increase reputation endlessly. This is done to deter malicious behavior, and to ensure any attempted whale attacks cannot buy their way back in.
The Foundation proposes an alternate conviction voting model. Voting power increases with each vote submitted that conforms with the outcome. This model also includes reputation as a determinant of voting power. For example, if you refer valuable projects to the ecosystem, solve tasks, or contribute to the overall network development, your voting power can increase.
The Routing Protocol can leverage Reputation Oracles to adjust voting power based on reputation. We hope this can foster excellent community contribution.
When a vote is in progress, conviction voting does as the name describes: it incentives the voter to vote with conviction. It does this by decreasing voting power if the voter changes their mind. This, along with the fact that voting power does not apply immediately, but rather ramps up over time, means it is less prone to both whale and last-minute attacks.
It is our adjustment of the regular conviction voting model. The alternate has two key distinctions:
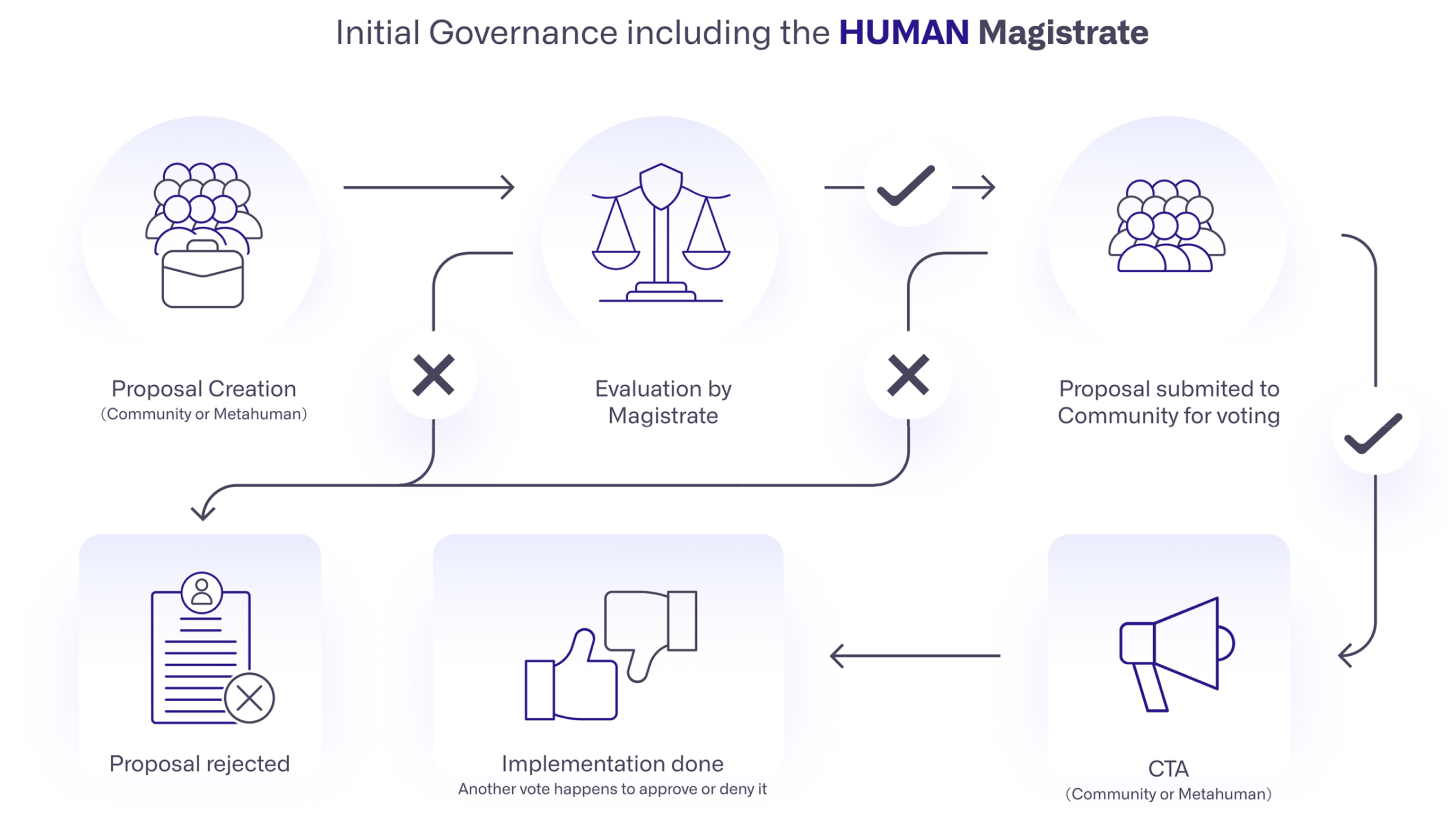
The HUMAN-RP Magistrate is a council of experts that receives, drafts, evaluates, and finally submits proposals to be voted on by the community. The first Magistrate will operate for one year only, and the council will be chosen by Metahuman. After that year, a community vote will decide on whether to confirm the members for another year, or to elect new members to the council.
In time, the community can submit proposals directly in addition to the proposals coming from Metahuman. One condition of proposals is to meet the minimum proposal threshold (1% of all voting power), which can also be achieved through delegation.
Before the vote goes to the community, a snapshot of voter weight is taken. Voting will be active for 14 (or 30) days. If at least 10% of voting power was with the decided outcome, the proposal will then get converted to a CTA, either to the community, or Metahuman, based on the proposal type.
We will utilize an adaption of Proof of HUMANity for users to sign a vote, or else their delegation.

A voter is presented with all options at the beginning of the vote and they can aportion their voting tokens to various options according to their preference. They could put 100% in one option, or split it over many, allowing for a less binary, more sophisticated voting model
The weight of the tokens on an option grows as you hold the conviction. The token weight grows according to a half life decay curve. This means that your preference gains weight over time, but only up to a certain point. The same decay curve can be used to reduce your token weight if you change preference, and lose conviction
This introduction of time is highly useful.
Most importantly, it guards against last minute voting attacks. In that sense, it also helps to prevent collusion. Because the reduction of voting power upon a preference change reduces voting power, we do not need to introduce token locks on a vote.
In alternate conviction voting, voters cannot use their tokens to vote on multiple proposals at the same time.
Because the voting model includes reputation and contribution, it strengthens community inclusion and participation.
This will be iterated over time. Whatever remit that is decided upon for voting, it must protect against network abuse. The Foundation is currently considering the following areas as suitable for voting remit: dApps, features, enhancements, and HUMAN Protocol versions.
For the latest updates on HUMAN Protocol, follow us on Twitter or join our Discord. Alternatively, to enquire about integrations, usage, or to learn more about HUMAN Protocol, get in contact with the HUMAN team.
Legal Disclaimer
The HUMAN Protocol Foundation makes no representation, warranty, or undertaking, express or implied, as to the accuracy, reliability, completeness, or reasonableness of the information contained here. Any assumptions, opinions, and estimations expressed constitute the HUMAN Protocol Foundation’s judgment as of the time of publishing and are subject to change without notice. Any projection contained within the information presented here is based on a number of assumptions, and there can be no guarantee that any projected outcomes will be achieved.
